Unlock Purity with Radiolite Filter aid Powder.
Radiolite Filter aid Powder is a premium-grade filtration agent that excels in removing impurities from liquids. With its fine particulate structure, Radiolite Filter aid Powder effectively captures sediments, toxins, and other unwanted materials, ensuring that your final product is of the highest quality.
Radiolite, Radiolite trading co, China (Imported Filter Aid Powder )
The filter aid powder used for filtration is Diatomaceous earth (DE), which consists of skeletal remains of single-celled plants called "diatoms" that contain silicon dioxide. The three classifications of Diatomaceous earth are natural, Calcined, and flux-Calcined. This product comes with quality certificates like HALAL, ISO, FCC KOSHER etc.


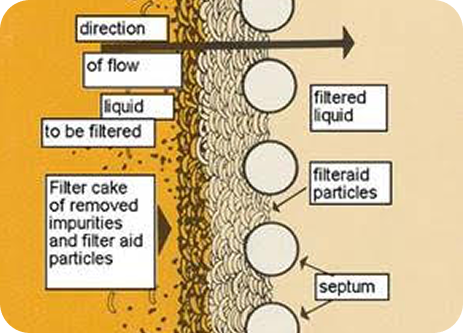
DE has a wide range of applications. Here are some common uses, with considerations for Radiolite where applicable:
Water Filtration: DE filters are used in swimming pools, aquariums, and for some types of water purification. The powder is mixed with the water, and then passed through a filter that traps the DE, along with any suspended particles. Radiolite is often used for water filtration.
Food and Beverage Filtration: DE is used in the filtration of beer, wine, juices, and other beverages to remove impurities and clarify the liquid.
Industrial Filtration: It is used in the filtration of various industrial products, from chemicals to pharmaceuticals.
Polishing: DE can be used as a mild abrasive in polishing compounds for metals, gemstones, and other materials.
Toothpaste: Some toothpastes may contain DE as a mild abrasive to help remove stains.
Spill Cleanup: DE is effective at absorbing spills of liquids, including oil, solvents, and other chemicals.
Cat Litter: DE can be used in cat litter to absorb odors and moisture.
Insecticide/Pest Control: Industrial grade DE can be used to control insects and pests, such as ants, bedbugs, and cockroaches. The abrasive nature of the DE damages the insects' exoskeletons, causing them to dehydrate and die.
Paint: DE can be added to paint as a filler and to improve its texture and durability.
Plastics and Rubber: It can be used as a filler in plastics and rubber products.
Soil Amendment: DE can be added to soil to improve drainage, aeration, and water retention.
Animal Feed: Food-grade DE can be added to animal feed as a source of silica and to help control internal parasites (though the effectiveness of this is debated, and it should not be the sole method).
Insulation: DE's heat resistance makes it suitable for insulation in some applications
Cosmetics: DE is sometimes used in cosmetics, such as facial masks and scrubs.
In Summary: Diatomaceous Earth, including Radiolite, is a versatile material with a wide variety of applications. From filtration and absorption to pest control and use as a filler, it has a number of industrial and consumer uses. However, it's crucial to be aware of the potential health risks associated with inhaling the dust and to always choose the appropriate grade of DE for the intended application.